What you need to know

Layoffs are making headlines, but most of them seem to be concentrated in one job category: technology.
The tech industry will increase layoffs by 649% in 2022, the highest rate since the dot-com bubble more than decades ago, according to The Challenger Report. More tech employees were laid off in 2022 than in 2020 and 2021 combined.
As of March 2024, more than 200 technology companies have laid off more than 50,800 employees in 2024, according to Layoffs.fyi.
While the labor sector as a whole looks strong from 2022 to 2023, layoffs in the technology sector tend to be the most visible. Tech giants have large workforces, so even a small layoff could mean thousands of people losing their jobs. Even after the dot-com bubble, the tech industry has remained resilient to economic challenges due to its large size and growing presence in personal and business applications. Most of these large-scale layoffs are from large, well-known companies.
Several factors can lead to tech layoffs, including the economy, inflation, rising interest rates, overemployment, and employment adjustments due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
AI is bisecting the technology job market as companies look to hire employees with AI-related skills. According to the President’s Economic Report, approximately 10% of U.S. jobs are at risk from AI disruption.
This disruption does not mean job losses, but could replace some of these workers and increase productivity. The biggest fear of job loss due to AI is people not learning how to use it.
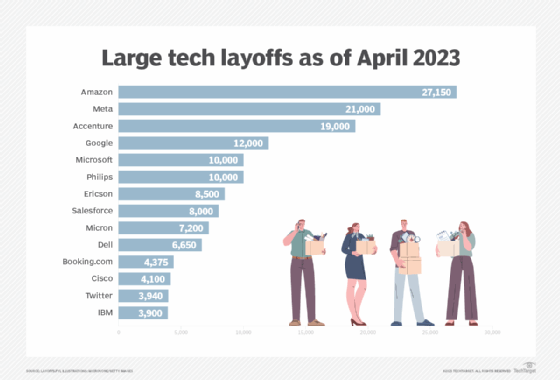
But IBM added fuel to the fire of AI job buys by announcing to employees at a conference that it plans to cut 3,900 jobs in marketing and communications, or 1.5% of its workforce. According to Bloomberg, the company also planned to stop hiring for positions that could be replaced by AI.
check out some Jobs that may be affected by AI.
economic downturn
The debate over the U.S. recession began when data from the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis showed the economy contracted for the second consecutive quarter in July 2022. Economists aren’t convinced, and news reports continue to echo fears of a recession. Other conditions also threaten the health of the economy, including the government debt ceiling, the war in Ukraine, the ongoing pandemic, and rising interest rates.
When revenues and profits decline, companies turn to layoffs to cut costs as a means of survival.
inflation
According to the Federal Reserve, when inflation hit the economy hard in June 2022, consumers experienced a 9.1% price increase, compared to the typical 2% annual rate of steady inflation. It is said that he did. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the inflation rate in 2022 was the highest in 40 years. The economy softened as people began to buy less in response to these higher prices. The cost of living has skyrocketed, forcing people and businesses to make cuts. As the prices of their services have increased, technology companies have had to evaluate and reduce prices as needed.
Businesses are looking to cut costs to cover increased spending due to inflation. Because firing employees is one of a company’s largest expenses, it is usually one of the first cost-cutting measures. When companies cut back on advertising, technology companies lose revenue. Technology companies like Meta, Google, Instagram, Snap, and ByteDance have business models that rely on advertising sales.
higher interest rate
The Fed will raise interest rates seven times in 2022 and could raise them even more in 2023. The Fed raises interest rates to slow economic growth and curb consumer and business spending, which reduces demand and ultimately lowers prices.
Higher interest rates affect the amount businesses want to borrow because they increase costs. These interest rate increases have a direct impact on venture capitalists (VCs) and other startup funding. When the future of the economy is uncertain, companies do not want to invest in risky areas. Economic uncertainty has caused companies to reevaluate their hiring and growth strategies.
The Fed has not changed interest rates as of March 2024.
investor pressure
Investors are hoping companies will cut costs as profits slow. Venture capital firms are concerned that profits will decline this year after a period of significant growth. For example, TCI Fund Management called on Google’s parent company, Alphabet, to reduce its workforce and take steps to improve profitability. Other big tech companies, including Meta and Microsoft, have also faced backlash from investors for having too many employees compared to other companies.
Overemployment during the pandemic
Part of the increase in layoffs is due to correcting overemployment. At the height of the pandemic, technology usage increased significantly as everything moved online. People are working remotely, shopping online, ordering groceries for pickup or delivery, streaming movies from home, and taking classes online rather than in person. As many people were quarantined and encouraged to stay at home, people spent more time online.
A surge in online activity has led to record profits for tech companies, and a hiring rush has begun to meet demand. Technology companies thought this would be the new normal and expanded their teams and grew rapidly.
Meta has nearly doubled its number of employees. In March 2020, Meta reported that it had 48,268 employees, which will grow to more than 80,000 by September 2022. In November 2022, the company announced that it would lay off 11,000 employees.
Some work is now returning to the way it was before the pandemic. When people have a hybrid work schedule, they don’t use technology as much as they would if they were working from home full time. Instead, they spend their time going to the store, traveling, attending sporting events, going to concerts, and eating at restaurants. As the demand for technical services decreased, the need for these new jobs also decreased.
Post-pandemic reality
Many of the employees hired during the pandemic were not entry-level employees, but experienced software engineers and developers earning six-figure salaries with generous benefits. Companies are facing increased redundancy and overstaffing. Companies had high hopes that this growth rate would continue. However, once restrictions were lifted, people returned to their pre-pandemic lifestyles. As they return to their previous work environments, major technology companies are cutting back on the extra employees they hired at the height of the pandemic.
Work-from-home technologies such as Google Meet, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom are still being used, but their numbers are decreasing as not all meetings are held solely online. Several employees have returned to the office to collaborate and share ideas.
mature industry
Technological layoffs may also be the result of an industry maturing or becoming more stable after rapid growth. Technology companies may not be on pace to attract as many new customers as many people have already adopted their services. Instead, tech companies may be looking beyond growth to product diversification and global expansion.
Silicon Valley bank failure
In March 2023, the technology industry faced a new obstacle when Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) collapsed due to lack of diversification and a run-in. SVB provided funding to high-tech startups when other banks were unwilling to take on higher risks.
SVB’s collapse will make more venture capitalists and banks wary of taking on risks in startups.
notable dismissal
Depending on the size of the company, large-scale layoffs can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of people, which can represent a large portion of the workforce. Some companies, such as Meta, have announced large-scale layoffs in several waves. Meta cut 11,000 employees in November 2022, followed by another 10,000 in March 2023. Amazon also made multiple large-scale job cuts: 10,000 in November 2022, 8,000 in January 2023, and 9,000 in March 2023.
Virgin Orbit has cut 85% of its workforce, or about 675 people. Virgin Orbit launched services for satellites and operates within the Virgin Group. Although their numbers are not as high as those at large tech companies, they still make up a large portion of the workforce.
Accenture also plans to cut 2.5% of its workforce (an estimated 19,000 people) in 2023.
Elon Musk said in an interview with the BBC that he has cut Twitter’s headcount by about 80%, cutting more than 6,000 people since taking office. When Musk took over, Twitter had about 8,000 employees, but after the layoffs, Twitter now has about 1,500 employees.
As of March 2024, personnel reductions continue. Most notably, 8,000 people were laid off from SAP, 4,250 from Cisco, 2,500 from PayPal, 1,500 from Expedia, and 1,000 from eBay.
Will layoffs spread to other industries?
According to CompTIA’s “State of the Tech Workforce” report, the total number of employees in the U.S. technology industry is approximately 8.9 million. Although there were a few layoffs in the technology and media industries, the rest of the labor market remained strong.
The US unemployment rate fell from 3.7% to 3.5% in December 2022. According to the BLS, this is the lowest level in 50 years. As of February 2024, the national unemployment rate rose to 3.9%.
According to the BLS, while big tech companies make headlines for cutting jobs, some small businesses are still hiring tech talent.
Source link




